Formation of States









Formation of States
How Were States To Be Formed: In 1920s, the Indian National congress -the main party of the freedom struggle- had promised that once the country won independence, each major linguistic group would have its own province.
India had been divided on the basis of religion : despite the wishes and efforts of Mahatma Gandhi, freedom had come not to one nation but to two . As result of the partition of India , more than a million people had been killed in the riots between Hindus and Muslims.
Both the Prime Minister Nehru and Deputy Prime Minister Vallabhbhai Patel were against the creation of linguistic states .
The first and last need of India at the present moment is that it should be made a nation every thing which helps the growth of nationalism has to go forward and everything which throws obstacles in its way has to be rejected we have applies this test to linguistic provinces.
The Congress leaders would now go back on their promise created great disappointment. The kannada speakers , Malayalam speakers , the Marathi speakers, had all looked forward to having their own states. The strongest all looked forward to having their own state. The strongest protest , however came from Telugu speaking districts of what was the Madras Presidency . when Nehru went to campaign there during the general elections of 1952he was met with black flags and slogans demanding " We want Andhra".
On 15 December 1952, fifty- eight days into his fast , Potti Sriramulu died. The protest were so widespread and intense that the central government was forced to give in to the demand. Thus, on 1october 1953, the new state of Andhra came into being , which subsequently became Andhra Pradesh.
After the creation of Andhra, other linguistic communities also demanded their own separate states.A states Reorganization Commission was set up, which submitted its report in 1956, recommending the redrawing of district and provincial boundaries to form compact provinces of Assamese, Bengali, Oriya, Tamil, Malayalam, Kannadaand Telgu speakers respectively. The large Hindi - speaking region of north India was also to be broken up into several states.In 1960, the bilingual state of Bombay was divided into separate states for Marathi and Gujarati speakers.
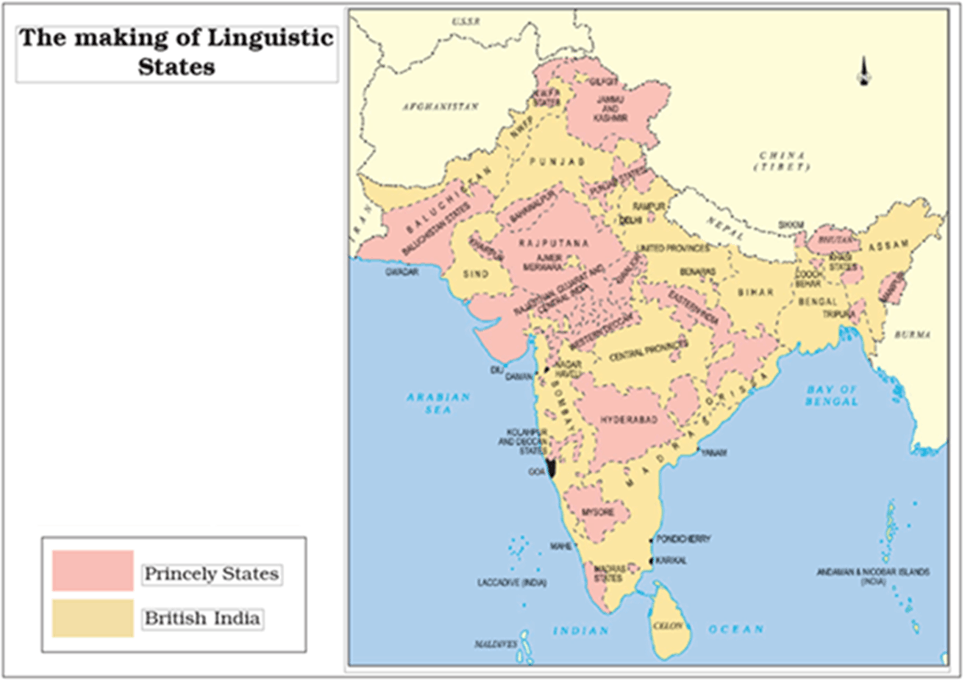
Indian Provinces and Princely states before 14 August 1947.

Indian states before 1 November1956

Who was the Deputy Prime Minister of the Independent India? | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
The Bhilai steel plant of _______ came to be seen as an important sign of development of modern India after Independence. | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Who were against the creation of linguistic states? | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation |
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
One of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.
